The 5 Key Parameters of Welding You Must Know
Updated: 13 Dec 2023
131
Welding is a versatile and essential process in various industries, from construction and manufacturing to automotive and aerospace. To achieve precise and high-quality welds, it is crucial to understand and optimize welding parameters.
In this blog post, we will dive into the world of welding parameters, exploring what they are, why they matter, and how to master them for optimal results.
What are Welding Parameters, and Why are they Important?
Welding parameters refer to the set of variables that significantly affect the outcome of the welding process. Each parameter determines a weld’s quality, strength, and efficiency. Understanding welding parameters deeply can improve your work in different types of welds.
Following are the importance of welding parameters through which you will better understand how parameters are efficient for welding.

© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
- Quality of Weld: Proper learning and optimization of welding parameters results in high-quality welds with excellent strength, durability, and visual appearance.
- Efficiency: These can enhance your efficiency by reducing the need for rework and decreasing the wastage of materials. This is particularly essential in industries where time and resources are valuable.
- Cost Savings: Fine-tuning welding parameters can reduce costs associated with consumables, energy consumption, and post-welding processes.
- Safety: Correct parameters contribute to a safe working environment by reducing the risk of defects in welding.
The 5 Key Parameters of Welding
Here are five breakdowns of welding that will help you to promote your welding to the next level. These parameters include;
- Current
- Length of Arc
- Angle
- Manipulation
- Speed
1. Current:
Current is the flow of electrical charges that play an essential role in welding. It is the powerhouse of welding. We measure current in ampere, represented by a capital “A.”
During welding, the magnitude of the current directly affects the heat generation. The correct current setting is crucial for controlling the weld bead size, penetration depth, and overall weld quality.
2. Length of Arc:
The arc length in welding refers to the distance between the welding electrode’s tip and the workpiece’s surface being welded. It is a critical parameter that significantly affects the stability, heat input, and overall weld quality.
Determining the Best Arc Length:
The ideal arc length varies depending on the welding process, electrode type, material thickness, and welding position. However, we provided a difference between short, medium, and long arc lengths as a general guideline.
A. Short Arc Length:
- Suitable for welding thin materials and achieving deep penetration.
- It is commonly used for precision work in processes like TIG welding.
B. Medium Arc Length:
- Offers a balanced compromise between penetration and bead width.
- It is preferred for many welding applications, providing a versatile option.
C. Long Arc Length:
- Suitable for welding thicker materials and producing a wider weld bead.
- It is commonly used in processes like MIG welding for higher deposition rates.
3. Angle:
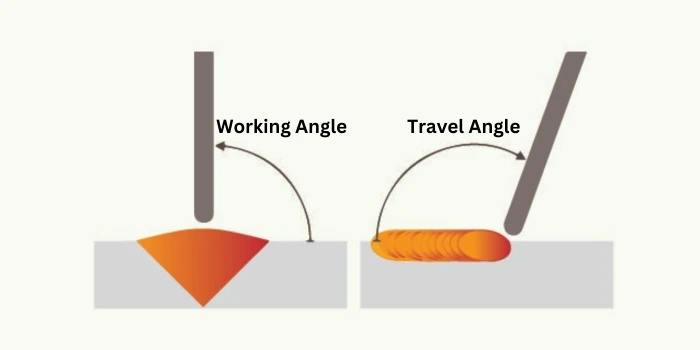
© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
In welding, the term “angle” refers to the welding torch’s or electrode’s orientation to the workpiece. Different welding processes and joint configurations require specific angles for optimal results. So, we have divided angles into types.
- Work Angle
- Travel Angle
a. Work Angle:
The work angle, also known as the “drag angle,” is the angle between the welding torch or electrode and the direction of travel. There are two primary types of work angles:
- Push Angle: The torch or electrode is angled in the direction of travel. This angle is often used in processes like MIG welding. It promotes better visibility of the weld pool and is effective for horizontal and flat welding positions.
- Pull Angle: The torch or electrode is angled against the direction of travel. This angle is common in TIG welding and is effective for vertical and overhead welding positions. It controls the weld pool and improves penetration.
b. Travel Angle:
The travel angle, also known as the “tilt angle,” is the angle between the welding torch or electrode and a line perpendicular to the joint being welded. There are two primary types of travel angles:
- Forehand Angle: The torch or electrode is inclined toward the direction of travel. This angle is suitable for producing shallow penetration and is often used for thin materials in processes like oxy-acetylene welding.
- Backhand Angle: The torch or electrode is inclined opposite to the direction of travel. This angle is commonly used in processes like TIG welding for deeper penetration and improved control over the weld pool.
4. Manipulation:
Manipulation is the technique used to move the welding torch (electrode) during the welding process. The skillful manipulation affects the weld’s bead structure, fusion, and overall aesthetics. Understanding and refining manipulation techniques are crucial for achieving consistent and high-quality welds.
5. Speed:
Welding speed or speed is the rate at which the weld is created, or speed refers to the rate at which the welding process is carried out. It is a critical parameter that affects both productivity and quality.
The right balance between speed and other parameters ensures proper heat input, penetration, and fusion. Adjusting welding speed according to the project’s specific requirements is essential for achieving optimal results.

© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
| Key Aspects of Welding Speed: |
|---|
Four key aspects of welding speed directly affect your welding aesthetics.
|
Exploring Additional Factors in Welding Parameters:
Voltage:

© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
Voltage determines the electrical potential difference between the welding electrode and the workpiece. Voltage is measured in volts and can be represented by the symbol “V.” It plays a significant role in controlling the weld bead size and penetration.
Electrode Type and Size:
The electrode type and size choice are critical as different electrodes have unique properties. Selecting the right electrode for the specific welding job influences factors such as metal deposition rate, weld penetration, and overall weld quality.
Shielding Gas:
Shielding gas is the gas that helps to protect the weld from atmospheric contaminants. It is used in MIG and TIG weddings for stability and cleanliness of the weld. This gaseous substance protects the molten weld pool from oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapour in the air.
How to Master Welding Parameters?
- 1. Training and Education: Invest in proper training and education for welders to ensure they understand the fundamentals of welding processes and parameters.
- 2. Experimentation: Conduct controlled experiments to determine the optimal parameters for specific materials, joint designs, and welding processes.
- 3. Documentation: Keep detailed records of welding parameters for each project. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future welding tasks.
- 4. Technology Integration: Technological advancements in welding equipment will allow you more precise control over parameters. Automated systems can enhance consistency and repeatability.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How do you select Welding Parameters?
- Material Type and Thickness: Different Materials and thicknesses require specific parameter adjustment.
- Joint Configuration: Welding parameters based on the joint design, such as fillet welds, groove welds, or butt joints.
- Welding Process: Choose parameters suitable to the welding process (MIG, TIG, Stick, etc.)
- Electrode or Filler Material: Select the proper electrode or filler material for the specific welding application.
- Welding Position: Different positions, such as flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead, require specific parameter changes for optimal results.
Which Parameter is mandatory in the Welding Process?
Current is a mandatory parameter in the welding process. It determines the amount of electrical charge flowing through the welding circuit, which generates heat during welding. Proper current adjustment is essential for controlling weld bead size, penetration depth, and overall weld quality.
The selection of appropriate current levels depends on factors such as material type, thickness, and welding process, making it an essential and foundational parameter in welding.
Final Thoughts:
Mastering welding parameters is a journey that involves understanding the science behind the process, continuous learning, and practical experience. By learning the essential parameters of welding, welders can achieve superior welds that meet the highest quality, efficiency, and safety standards.
As technology continues to evolve, informing about the latest advancements will be crucial for those seeking to become experts in the art of welding.
Besides, if you are a welder and have extra information related to welding parameters, you can share it through the comment section. This will help our users to get more information about this topic. We also solve unexpected welding-related problems, so remember to contact us.
Our team will contact you as soon as possible. Spread love by sharing this piece of information with your welding community. Take Care of yourself and your family. Thank you for visiting our website.
Please Write Your Comments