MIG Welding With 100% Argon Shielding Gas | The Ultimate Guide
Updated: 7 Dec 2023
196
MIG welding, also known as GMAW, is a popular welding process that uses a consumable wire electrode to join two or more metal pieces. In this process, shielding gas is one of the most crucial and widely utilized elements, which is vital in safeguarding the weld pool from environmental contaminants.
Among the various gases available for welding, the use of 100% argon has become increasingly popular, particularly in specific applications. This blog post will cover all queries, essential considerations, benefits, and tips for MIG welding with 100% argon.
The Role of Argon in MIG Welding:
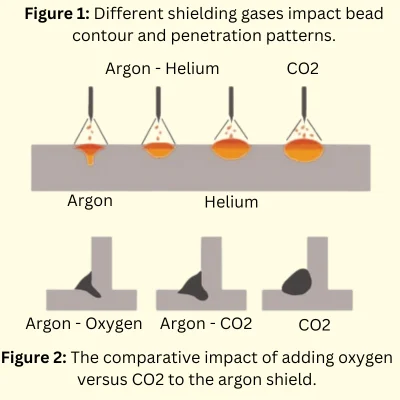
Argon is a noble gas, inert (neutral) in nature, that offers excellent shielding properties, preventing oxidation and other atmospheric contaminants from damaging the quality of the weld. Although MIG welding is usually carried out using a blend of Argon and carbon dioxide, there are situations where the preferred option is 100% argon.

© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
Can You MIG Weld Steel Using 100% Argon Gas?
Yes, it is possible to MIG weld steel using 100% argon gas, but it’s not the most common choice. Pure Argon is often used in TIG welding. In contrast, MIG welding typically involves a mixture of Argon/carbon dioxide or Argon/oxygen for better arc stability and weld penetration. The specific gas selection depends on the type of steel, thickness, and welding conditions.
Benefits of MIG Welding with Pure Argon:
100% Argon is not suitable for MIG welding, but in some cases, you can use it where you will see the following benefits.
© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
1. Cleaner Welds:
Argon provides a cleaner environment for welding by minimizing the presence of oxygen and other impurities. This is crucial for materials that are sensitive to oxidation, such as aluminum.
2. Reduced Spatter:
Welding with 100% argon often reduces spatter and the cleanup process. This is beneficial in applications where aesthetics and quality are essential.
3. Improved Arc Stability:
Argon provides a stable welding arc, enhancing control and accuracy during welding. This is particularly helpful for detailed welding projects.
More about Pure Argon Shielding Gas:
- The elemental symbol is “Ar”.
- We can obtain pure Argon from the atmosphere through air separation plants.
- It pushes away air effectively because it is heavier and denser than the surrounding air.
- Commonly used in TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding.
- It’s not the typical choice for MIG welding.
- Suitable for welding non-ferrous metals like aluminum and magnesium.
Considerations When MIG Welding with Pure Argon:
In exceptional cases, if you desire to MIG weld with 100% Argon, it is crucial to consider the following considerations.
1. Material Compatibility:
While 100% argon is suitable for welding certain materials like aluminum, it is not the best choice for all metals. Consider the specific requirements of the welded material and check the welding chart for guidance.
2. Thickness of Material:
Thicker materials may require a different gas mixture for good results. Check out the thickness of the metal and adjust the welding parameters accordingly.
The YouTube video below shows the practical representation of MIG welding with Pure Argon.
Tips for MIG Welding with 100% Argon:
- Optimal Flow Rate: Set the argon flow rate according to the welding machine specifications and the welded material. A consistent and appropriate flow rate is essential for effective shielding.
- Proper Technique: Ensure proper welding techniques, including gun angle and travel speed. These factors play an essential role in achieving high-quality welds.
- Equipment Calibration: Regularly calibrate and maintain your welding equipment to ensure accurate and reliable performance. This includes checking the gas flow regulator, wire feed speed, and voltage settings.
Why Is 100% Argon So Different? The drawback of Pure Argon in MIG Welding
In consideration of MIG welding, some essential points make 100% Argon different from a mixture of Argon and carbon dioxide. These characteristics are given below;
- 1. Instability of Arc: 100% Argon tends to provide a less stable arc than a mixture of Argon and carbon dioxide in MIG welding.
- 2. Low Thermal Conduction: Pure Argon has low thermal conduction, which quickly cools down and, as a result, gives you narrow and reduced penetration.
- 3. Low Ionization Potential: Pure Argon can decrease the arc voltage and power due to the low ionization, which produces a less stable arc.
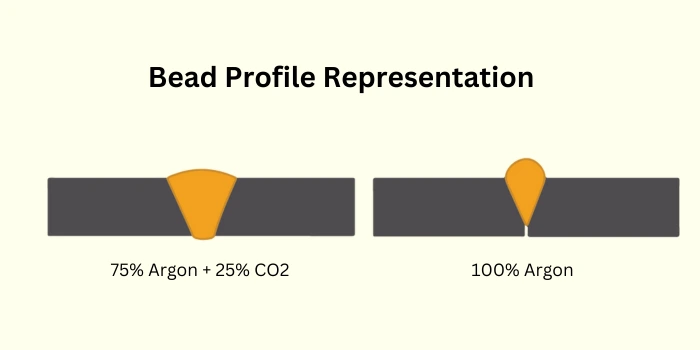
- 4. Production of Narrow and Long Bead: Using pure Argon in MIG welding can produce a narrow, long bead.
| Using 100% Argon To MIG Weld Base Metals: |
|---|
You can use 100% argon on some base metals to mig weld, and these base metals are;
|
CO2 and Argon Blend Work Better To MIG Weld Steel:
Indeed, CO2 and argon blends are preferred for MIG welding steel. This 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide mixture offers enhanced arc stability, penetration, and weld quality. The combination provides optimal performance for welding various types of steel, making it a popular choice in MIG welding applications.
© weldingvilla.com – Image usage rights
Frequently Asked Questions:
What percentage of Argon for MIG welding?
The percentage of Argon for MIG welding typically varies based on the specific welding application and materials involved. Commonly used mixtures include 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide for general steel welding. Pure Argon is often preferred for welding non-ferrous metals like aluminum.
How About MIG Welding Stainless Steel With 100% Argon?
MIG welding stainless steel with 100% argon is generally not recommended. Pure Argon is suitable for TIG welding stainless steel, while MIG welding of stainless steel typically requires a shielding gas mixture.
Commonly used mixtures include 90% helium and 10% argon or a combination of Argon (90%), helium (7.5%), and carbon dioxide(2.5%). These mixtures provide better penetration and overall welding performance for stainless steel applications.
Final Thoughts:
MIG welding with completely pure Argon is not the conventional choice for steel welding. It has niche applications with materials like aluminum sensitive to oxidation. However, it’s crucial to consider the drawbacks of using pure Argon in MIG welding, such as arc instability and reduced penetration. Choosing between 100% argon and gas mixtures ultimately depends on the specific welding requirements and the type of joining metals.
Finally, you understand entirely pure Argon, but if you still need clarification, you can ask in the comment section or the Contact Us page. Our team will contact you ASAP. If this blog post is helpful for welders like you, share it with your welding community. Thank you for visiting our website, see you soon, Bye Bye.
Please Write Your Comments